Product Description
|
Product Name |
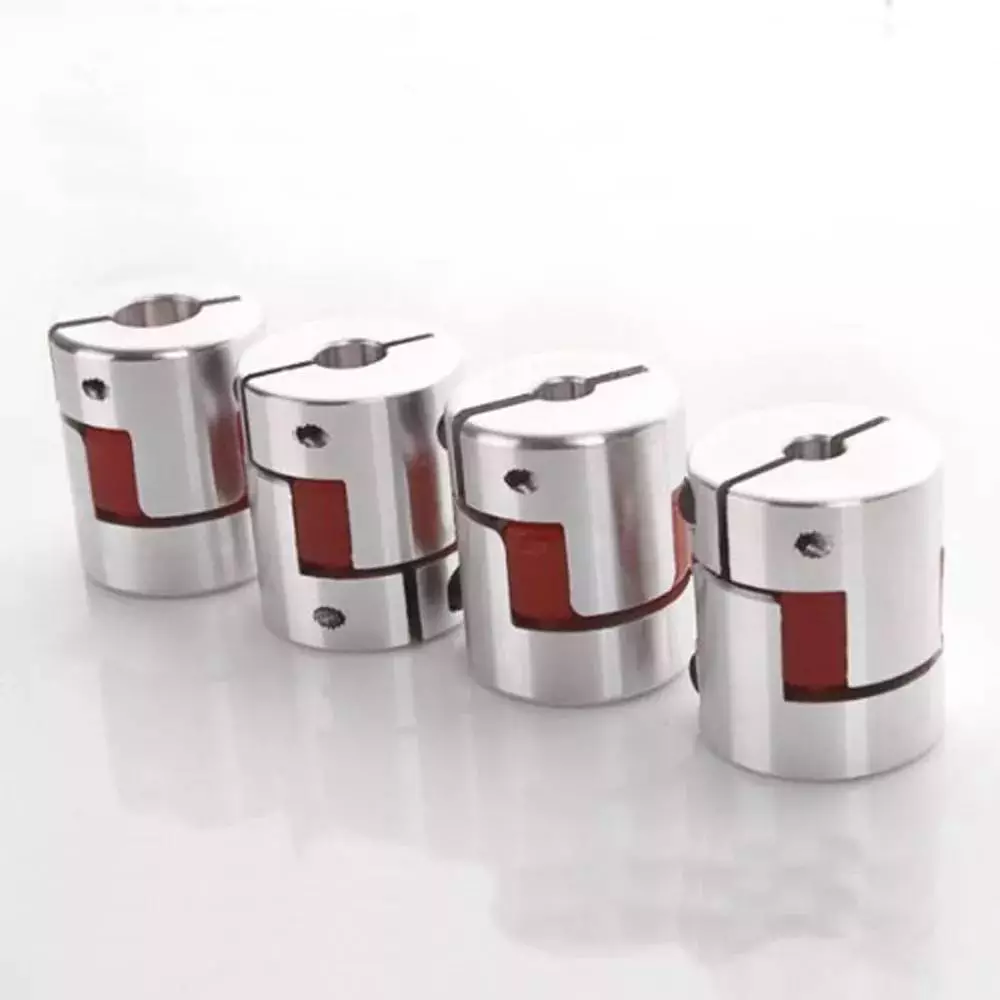
Aluminum Alloy Elastic Winding Encoder Coupler Flexible Shaft Spline Clamp Beam Couplings |
|
Material |
Aluminum alloy |
|
Surface treatment |
Natural color anode |
|
Customized service |
Support light customization and logo customization |
|
Remarks |
The default engraving brand name and size of the product. If you need not engraving, please contact the customer service for comments |
| Packaging Details | Carton box with anti-static package,carton plus with wooden case. |
| Main Products | Shaft Parts, Timing Belt Pulley, Gears, CNC Machining Parts, Sheet Metal Fabrication |
| Certifications(2) | ISO9001:2015, IPMS |
| Applicable Industries | Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Food & Beverage Factory, Farms |
| Supply Ability | 100000 Piece/Pieces per Month |
| Dimension | oem provided |
| Surface finish | anodized |
| Lead Time | 25 days |
| Application | Furniture,cabinet |
| Custom | OEM and ODM services are welcome,we can make cutom LOGO and products according to customer’s requests. |
| Quality control Our | Finished product inspection,Warranty available |
| service | Swiss machining;deburring;lathe/turning;5 axis;micromachining |
| Color |
silver,gold,black,red,bulue,and according to the customer requests. |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can mechanical couplings compensate for shaft misalignment and vibrations?
Yes, mechanical couplings can compensate for shaft misalignment and vibrations to a certain extent, depending on their design and flexibility. The ability to accommodate misalignment and dampen vibrations is a key feature of many mechanical couplings, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Here’s how they achieve these compensatory functions:
1. Shaft Misalignment Compensation:
Mechanical couplings, especially flexible couplings, are designed to handle various types of shaft misalignment, which can occur due to installation errors, thermal expansion, or dynamic loads. The following types of misalignment can be compensated by specific couplings:
- Angular Misalignment: Some flexible couplings, like Oldham couplings or universal couplings (Hooke’s joints), can accommodate angular misalignment between the shafts.
- Parallel Misalignment: Elastomeric or rubber couplings, such as jaw couplings or tire couplings, can compensate for parallel misalignment.
- Axial Misalignment: Certain types of flexible couplings, like beam couplings or bellows couplings, can tolerate axial misalignment.
2. Vibration Damping:
Flexible couplings are particularly effective at dampening vibrations in mechanical systems. The flexible elements or materials used in these couplings absorb vibrations caused by imbalances or dynamic loads, reducing the transmission of vibrations to connected components. This feature helps in:
- Reducing wear and fatigue on bearings, gears, and other components.
- Minimizing noise and improving the overall system’s smooth operation.
- Protecting sensitive equipment from excessive vibrations.
3. Limitations:
While mechanical couplings can compensate for some degree of misalignment and dampen vibrations, they have limitations:
- Excessive misalignment: Couplings have their specified misalignment limits. If misalignment exceeds these limits, it may lead to premature wear or coupling failure.
- High-frequency vibrations: Some couplings may not effectively dampen high-frequency vibrations, and additional measures might be needed to control vibrations in such cases.
- Resonance: Couplings can introduce or exacerbate resonance in a system if not selected properly for the application.
Overall, mechanical couplings with misalignment compensation and vibration damping properties play a crucial role in ensuring smooth and reliable operation of mechanical systems. Proper selection and installation of the appropriate coupling based on the specific application requirements are essential to maximize their compensatory capabilities.
“`
Explaining the impact of mechanical coupling wear on system efficiency.
Mechanical coupling wear can have a significant impact on the efficiency and performance of a mechanical system. As couplings wear over time, several factors come into play that affect the overall efficiency of the system:
1. Loss of Torque Transmission:
As couplings wear, they may develop gaps or play between the mating components. This can result in a loss of torque transmission between the connected shafts. Reduced torque transmission leads to diminished power transfer and can result in inadequate performance of the system, especially in high-torque applications.
2. Misalignment Issues:
Worn couplings may not effectively compensate for misalignments between the connected shafts. Misalignment can cause additional stress on bearings, gears, and other components, leading to increased wear and reduced system efficiency. It can also result in increased vibration and noise, further impacting the system’s performance.
3. Vibration and Resonance:
Wear in flexible couplings can lead to increased vibration and resonance within the system. Excessive vibrations can cause premature failure of components and reduce the overall system efficiency. Vibrations can also create a safety hazard for operators and equipment.
4. Energy Losses:
Worn couplings may introduce energy losses due to friction and slippage. These losses decrease the overall efficiency of the system and result in additional energy consumption to achieve the desired output.
5. Increased Maintenance Costs:
As couplings wear, they may require more frequent maintenance and replacement. The increased downtime for maintenance and the cost of replacing worn couplings can impact the system’s productivity and increase operational expenses.
6. Reduced System Reliability:
Worn couplings are more prone to sudden failures, leading to unplanned downtime. Unreliable systems can disrupt production schedules, affect product quality, and result in lost revenue.
7. Safety Concerns:
Worn couplings can compromise the safety of personnel and equipment. They may lead to unexpected failures, flying debris, or even catastrophic accidents in severe cases.
8. Impact on Product Quality:
In certain industries, like precision manufacturing or aerospace, system efficiency directly affects product quality. Worn couplings can cause inaccuracies, leading to subpar products and potential rework or rejection.
To maintain optimal system efficiency and prevent these issues, it is crucial to perform regular inspections and maintenance of mechanical couplings. Timely replacement of worn couplings and adherence to manufacturer’s guidelines for installation and maintenance can significantly contribute to the overall efficiency, reliability, and safety of the mechanical system.
“`
Advantages of using mechanical couplings in power transmission systems.
Mechanical couplings offer several advantages when used in power transmission systems, making them a preferred choice in various industrial applications. Some of the key advantages include:
- Torque Transmission: Mechanical couplings efficiently transmit torque from one shaft to another, enabling the transfer of power between different components of the system.
- Misalignment Compensation: Many mechanical couplings can accommodate axial, radial, and angular misalignments between connected shafts, ensuring smooth operation even when precise alignment is challenging to achieve or maintain.
- Vibration Damping: Some types of mechanical couplings, particularly flexible couplings, dampen vibrations caused by imbalances or load fluctuations. This feature reduces wear on components and improves overall system stability.
- Shock Absorption: Certain flexible couplings have the ability to absorb shocks and impacts, protecting the connected equipment from sudden force variations and preventing damage.
- Easy Installation: Mechanical couplings are generally easy to install and replace. Their modular design simplifies maintenance and reduces downtime in case of coupling failure.
- Load Distribution: Mechanical couplings evenly distribute the load between connected shafts, preventing premature wear and reducing the chances of component failure.
- Compact Design: Mechanical couplings come in various compact designs, allowing for efficient power transmission without adding significant bulk to the system.
- Customizability: Manufacturers offer a wide range of mechanical couplings with different sizes, materials, and features to meet specific application requirements, giving engineers the flexibility to choose the most suitable coupling for their systems.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Mechanical couplings are generally cost-effective compared to more complex power transmission methods, making them a practical choice for many industrial applications.
- Safety: Some mechanical couplings, like shear-pin or torque-limiting couplings, act as safety features, disconnecting or slipping when the system experiences overload, preventing damage to expensive components.
These advantages make mechanical couplings indispensable in power transmission systems across various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, marine, and more. Their ability to efficiently transmit power, accommodate misalignments, and protect the equipment ensures reliable and smooth operation of mechanical systems, contributing to overall system performance and longevity.
“`

editor by CX 2024-05-08
China OEM Aluminum Alloy Elastic Winding Encoder Coupler Flexible Shaft Spline Clamp Beam Couplings spline coupling
Product Description
|
Product Name |
Aluminum Alloy Elastic Winding Encoder Coupler Flexible Shaft Spline Clamp Beam Couplings |
|
Material |
Aluminum alloy |
|
Surface treatment |
Natural color anode |
|
Customized service |
Support light customization and logo customization |
|
Remarks |
The default engraving brand name and size of the product. If you need not engraving, please contact the customer service for comments |
| Packaging Details | Carton box with anti-static package,carton plus with wooden case. |
| Main Products | Shaft Parts, Timing Belt Pulley, Gears, CNC Machining Parts, Sheet Metal Fabrication |
| Certifications(2) | ISO9001:2015, IPMS |
| Applicable Industries | Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Food & Beverage Factory, Farms |
| Supply Ability | 100000 Piece/Pieces per Month |
| Dimension | oem provided |
| Surface finish | anodized |
| Lead Time | 25 days |
| Application | Furniture,cabinet |
| Custom | OEM and ODM services are welcome,we can make cutom LOGO and products according to customer’s requests. |
| Quality control Our | Finished product inspection,Warranty available |
| service | Swiss machining;deburring;lathe/turning;5 axis;micromachining |
| Color |
silver,gold,black,red,bulue,and according to the customer requests. |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

What are the best practices for installing a mechanical coupling correctly?
Proper installation of a mechanical coupling is essential to ensure its optimal performance and prevent premature failure. Follow these best practices when installing a mechanical coupling:
1. Clean the Shaft Ends:
Before installation, ensure that the shaft ends are clean and free from dirt, debris, and any old coupling remnants. Clean the shafts using a suitable solvent if necessary.
2. Verify Shaft and Bore Dimensions:
Check the dimensions of the shaft and bore to ensure they match the coupling’s specifications. Ensure that the shaft and bore diameters, keyway sizes, and lengths are correct for the specific coupling.
3. Lubricate Contact Surfaces:
Apply a thin layer of appropriate lubricant to the contact surfaces of the shaft and coupling bore. This helps in easy installation and minimizes the risk of galling or damage during assembly.
4. Align Shaft and Coupling:
Align the shafts and coupling properly before installing. Avoid forcing the coupling onto the shaft; it should slide smoothly into position.
5. Use Proper Installation Tools:
Use the recommended installation tools or methods provided by the coupling manufacturer. Using improper tools may lead to damage or misalignment of the coupling.
6. Tighten Fasteners Gradually and Evenly:
If the coupling uses set screws, bolts, or any fasteners, tighten them gradually and evenly in a criss-cross pattern. This ensures uniform distribution of pressure and prevents distortion.
7. Check for Proper Keyway Fit:
If the coupling utilizes keyways, ensure that the keys fit snugly into both the shaft and the coupling keyway to prevent movement or slippage.
8. Verify Proper Torque:
If the coupling requires a specific torque value for installation, use a torque wrench to achieve the correct tightening. Avoid over-torquing as it may damage the coupling or cause premature wear.
9. Inspect for Runout and Alignment:
After installation, inspect the coupling for runout and alignment. Verify that the shafts are concentric and parallel, as misalignment can lead to premature coupling failure.
10. Conduct Regular Inspections:
Perform regular inspections and maintenance of the coupling during its operational life. Check for signs of wear, misalignment, or damage and address any issues promptly.
Adhering to these best practices ensures that the mechanical coupling is installed correctly and operates as intended. Proper installation increases the coupling’s longevity, minimizes the risk of downtime, and contributes to the overall efficiency and reliability of the mechanical system.
“`
Are there any safety considerations when working with mechanical couplings?
Yes, working with mechanical couplings involves some safety considerations to prevent accidents and ensure the well-being of personnel. Here are important safety measures to keep in mind:
1. Lockout/Tagout Procedures:
Prior to working on machinery with mechanical couplings, implement lockout/tagout procedures to ensure that the equipment is isolated from its power source and cannot be accidentally energized during maintenance or repair activities.
2. Proper Training:
Ensure that personnel working with mechanical couplings receive proper training on safe handling, installation, and maintenance procedures. Adequate knowledge of coupling types, torque limits, and alignment techniques is crucial to avoid accidents.
3. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves, safety goggles, and hearing protection, when installing or inspecting couplings. This helps prevent injuries from sharp edges, rotating parts, or potential flying debris.
4. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and instructions for the specific coupling being used. Proper installation torque, maintenance schedules, and safety precautions provided by the manufacturer should be strictly adhered to.
5. Inspections:
Regularly inspect the couplings for signs of wear, misalignment, or damage. Any worn or damaged couplings should be replaced promptly to prevent failures during operation.
6. Avoid Overloading:
Do not exceed the torque and speed limits specified by the manufacturer for the coupling. Overloading the coupling can lead to premature failure and potential safety hazards.
7. Preventive Maintenance:
Implement a preventive maintenance program to regularly check and service the couplings as recommended by the manufacturer. Proper maintenance can extend the life of the coupling and prevent unexpected failures.
8. Proper Storage:
Store spare couplings in a safe and dry environment, away from potential damage or exposure to harmful substances. Protect the couplings from corrosion and contamination.
9. Emergency Procedures:
Have emergency procedures in place in case of coupling failure or accidents. Employees should know how to respond to unexpected incidents safely.
10. Proper Lifting and Handling:
When installing or removing heavy couplings, use appropriate lifting equipment and techniques to prevent strain or injuries.
By following these safety considerations, workers can reduce the risk of accidents and ensure a safe working environment when dealing with mechanical couplings.
“`
How does a mechanical coupling facilitate the connection between two shafts?
A mechanical coupling plays a critical role in connecting two shafts in a mechanical system and enabling the transmission of torque and motion between them. The process of how a mechanical coupling facilitates this connection can be explained as follows:
1. Physical Linkage:
A mechanical coupling physically links the two shafts together. It consists of two mating components that fit over the respective shaft ends, ensuring a secure connection.
2. Torque Transmission:
When the motor or driving shaft rotates, it generates torque. This torque is transmitted through the mechanical coupling to the driven shaft, causing it to rotate as well.
3. Keyways or Spline Connection:
Many mechanical couplings use keyways or splines to enhance the connection between the shafts. Keyways are slots cut into the shaft and coupling, and a key is inserted to prevent relative motion between the two components.
4. Compression or Expansion Fit:
In some couplings, the connection between the shafts is achieved through a compression or expansion fit. The coupling is designed to be slightly smaller or larger than the shaft diameter, creating a tight fit when assembled.
5. Set Screws or Bolts:
Set screws or bolts are often used in mechanical couplings to secure the coupling tightly to the shafts. These screws apply pressure to prevent any relative movement between the coupling and the shafts during operation.
6. Flexible Elements:
Flexible couplings feature elements made of materials like rubber or elastomers that can bend or flex. These elements accommodate misalignment between the shafts while maintaining the connection and transmitting torque.
7. Key Features:
Certain types of couplings, such as gear couplings or disc couplings, utilize teeth or gear features to achieve a strong and precise connection between the shafts. These key features ensure a positive engagement, enhancing torque transmission.
In summary, a mechanical coupling serves as the link between two rotating shafts, enabling them to function together as a single unit. Whether through a tight compression fit, keyways, or flexible elements, the coupling ensures a secure and efficient connection, allowing torque to be transmitted from one shaft to the other, and enabling the mechanical system to perform its intended function reliably.
“`

editor by CX 2024-04-25
China Professional Aluminum Alloy Elastic Winding Encoder Coupler Flexible Shaft Spline Clamp Beam Couplings spline coupling
Product Description
|
Product Name |
Aluminum Alloy Elastic Winding Encoder Coupler Flexible Shaft Spline Clamp Beam Couplings |
|
Material |
Aluminum alloy |
|
Surface treatment |
Natural color anode |
|
Customized service |
Support light customization and logo customization |
|
Remarks |
The default engraving brand name and size of the product. If you need not engraving, please contact the customer service for comments |
| Packaging Details | Carton box with anti-static package,carton plus with wooden case. |
| Main Products | Shaft Parts, Timing Belt Pulley, Gears, CNC Machining Parts, Sheet Metal Fabrication |
| Certifications(2) | ISO9001:2015, IPMS |
| Applicable Industries | Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Food & Beverage Factory, Farms |
| Supply Ability | 100000 Piece/Pieces per Month |
| Dimension | oem provided |
| Surface finish | anodized |
| Lead Time | 25 days |
| Application | Furniture,cabinet |
| Custom | OEM and ODM services are welcome,we can make cutom LOGO and products according to customer’s requests. |
| Quality control Our | Finished product inspection,Warranty available |
| service | Swiss machining;deburring;lathe/turning;5 axis;micromachining |
| Color |
silver,gold,black,red,bulue,and according to the customer requests. |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Comparing mechanical couplings with other types of couplings in performance.
Mechanical couplings are an essential component in power transmission systems, and they are often compared with other types of couplings based on their performance characteristics. Let’s explore how mechanical couplings compare with some other common coupling types:
1. Mechanical Couplings vs. Fluid Couplings:
Fluid couplings use hydraulic fluid to transmit torque between the input and output shafts. They offer smooth torque transmission and can act as a torque limiter, protecting the connected equipment from overloads. However, they have some energy losses due to fluid turbulence, which slightly reduces their efficiency compared to mechanical couplings. Mechanical couplings, on the other hand, provide direct and efficient torque transmission without any energy losses due to fluid friction.
2. Mechanical Couplings vs. Magnetic Couplings:
Magnetic couplings use magnetic fields to transfer torque from one shaft to another. They are commonly used in applications where a hermetic seal is required, such as in pumps and mixers. Magnetic couplings have the advantage of being completely leak-proof, unlike mechanical couplings that may require seals in certain applications. However, magnetic couplings have a lower torque capacity compared to many mechanical couplings, and their efficiency can be affected by variations in magnetic field strength and alignment.
3. Mechanical Couplings vs. Hydraulic Couplings:
Hydraulic couplings use hydraulic fluid to transmit torque. They offer high torque capacity and the ability to slip during overloads, acting as a safety feature. However, hydraulic couplings can have energy losses due to fluid friction, making them slightly less efficient than mechanical couplings. Mechanical couplings do not have energy losses related to fluid friction and provide direct torque transmission, making them more efficient in this regard.
4. Mechanical Couplings vs. Electrical Couplings:
Electrical couplings use electromagnetic fields to transfer torque. They are commonly used in high-precision and high-speed applications, such as robotics and aerospace systems. Electrical couplings can have high torque capacity and precise control over torque transmission. However, they require electrical power to function, which may not be suitable for all applications. Mechanical couplings are self-contained and do not require additional power sources, making them more suitable for various types of machinery and equipment.
5. Mechanical Couplings vs. Friction Couplings:
Friction couplings use friction between contacting surfaces to transmit torque. They are simple in design and can slip during overloads, providing protection against excessive loads. However, friction couplings can experience wear and require periodic maintenance. Mechanical couplings, depending on their type, may have a more robust design and may not experience as much wear under normal operating conditions.
In summary, mechanical couplings offer direct and efficient torque transmission without energy losses related to fluid friction or magnetic fields. While other coupling types may have specific advantages in certain applications, mechanical couplings remain a versatile and widely used choice in various industries due to their reliability, simplicity, and ease of maintenance.
“`
What are the temperature and environmental limits for mechanical couplings?
Mechanical couplings are designed to operate within specific temperature and environmental limits to ensure their performance and longevity. These limits can vary depending on the coupling type, materials, and the specific application. Here are some general considerations regarding temperature and environmental limits for mechanical couplings:
Temperature Limits:
Mechanical couplings are typically rated to handle a specific temperature range. Extreme temperatures can affect the mechanical properties of the coupling’s materials and lead to premature wear or failure.
High-Temperature Applications: In high-temperature environments, couplings made from materials with high-temperature resistance, such as stainless steel or high-temperature alloys, are often used. These couplings can withstand elevated temperatures without experiencing significant degradation.
Low-Temperature Applications: In low-temperature environments, special consideration must be given to the materials’ brittleness and the potential for reduced flexibility. Some couplings may require low-temperature lubricants or preheating to ensure proper operation in cold conditions.
Environmental Limits:
Mechanical couplings can be exposed to various environmental factors that may impact their performance. Manufacturers specify the environmental limits for their couplings, and it is essential to adhere to these guidelines.
Corrosive Environments: In corrosive environments, such as those with exposure to chemicals or saltwater, couplings made from corrosion-resistant materials, like stainless steel or nickel alloys, are preferred. Proper seals and coatings may also be necessary to protect the coupling from corrosion.
High Humidity or Moisture: Excessive humidity or moisture can lead to rust and corrosion, especially in couplings made from ferrous materials. In such environments, using couplings with proper corrosion protection or moisture-resistant coatings is advisable.
Outdoor Exposure: Couplings used in outdoor applications should be designed to withstand exposure to weather elements, such as rain, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations. Enclosures or protective covers may be necessary to shield the coupling from environmental factors.
Special Applications:
Certain industries, such as food and pharmaceutical, have strict hygiene requirements. In such cases, couplings made from food-grade or hygienic materials are utilized to prevent contamination and meet regulatory standards.
It is crucial to consult the coupling manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines to determine the appropriate temperature and environmental limits for a specific coupling. Adhering to these limits ensures the coupling’s proper operation and longevity in its intended application, reducing the risk of premature wear and failures caused by extreme conditions.
“`
How do splined couplings work?
Splined couplings work by using interlocking ridges or teeth on the coupling and the connected shafts to transmit torque while allowing some degree of misalignment and axial movement. The operation of splined couplings can be understood in the following steps:
1. Spline Design:
The coupling and the shafts are machined with matching ridges or teeth along their surfaces. These ridges form the spline. There are various spline designs, including involute splines, straight-sided splines, and serrated splines, each with different tooth profiles and configurations.
2. Engagement:
When the splined coupling is fitted onto the shafts, the ridges on the coupling engage with the corresponding grooves on the shafts, creating a secure and positive connection. The engagement can be internal, where the coupling fits inside the shafts, or external, where the coupling fits over the shafts.
3. Torque Transmission:
When torque is applied to one of the shafts, the ridges on the coupling transmit the torque to the other shaft, allowing rotational motion to be transferred between the two shafts.
4. Misalignment Compensation:
Splined couplings can accommodate a small amount of misalignment between the shafts. This misalignment can be angular, where the shafts are not perfectly aligned, or parallel, where the shafts are slightly offset from each other. The splined design allows the coupling to flex slightly, accommodating these misalignments and reducing stress on the shafts and other components.
5. Axial Movement:
Some spline couplings, such as spline shafts, can also allow for limited axial movement. This axial play is useful in applications where thermal expansion or contraction of the shafts may occur, preventing excessive forces on the system.
Splined couplings are commonly used in precision motion control systems, automotive drivetrains, industrial machinery, and other applications where accurate torque transmission and flexibility in alignment are essential. Proper machining and assembly are critical to ensuring precise engagement and reliable operation of splined couplings in various mechanical systems.
“`

editor by CX 2024-04-15
China wholesaler Aluminum Motor Shaft Coupler D19L25 Flexible Spline Shaft Couplings spline coupling
Product Description
Product Description
|
Product name |
Chain coupling |
|||
|
Material |
Carbon steel material |
|||
|
Structure |
Roller chain+sprocket+cover |
|||
|
Size |
KC3012, KC4012, KC4014, KC4016, KC5014, KC5016, KC5018, KC6018, KC6571, KC6571, KC8018, KC8571, KC8571, KC1571, KC12018, KC12571, KC16018, KC16571, KC20018, KC20571, KC24026 |
|||
|
Other type |
Flexible coupling |
|||
|
Application |
Shaft transmission |
|||
|
Feature |
High performance, light weight, convenient assembly |
|||
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
ZheJiang Haorongshengye Electrical Equipment Co., Ltd.
1. Was founded in 2008
2. Our Principle:
“Credibility Supremacy, and Customer First”
3. Our Promise:
“High quality products, and Excellent Service”
4. Our Value:
“Being Honesty, Doing the Best, and Long-lasting Development”
5. Our Aim:
“Develop to be a leader in the power transmission parts industry in the world”
|
6.Our services: |
1).Competitive price |
|||
|
2).High quality products |
||||
|
3).OEM service or can customized according to your drawings |
||||
|
4).Reply your inquiry in 24 hours |
||||
|
5).Professional technical team 24 hours online service |
||||
|
6).Provide sample service |
||||
Main products
Machines
Exbihition

Comparing mechanical couplings with other types of couplings in performance.
Mechanical couplings are an essential component in power transmission systems, and they are often compared with other types of couplings based on their performance characteristics. Let’s explore how mechanical couplings compare with some other common coupling types:
1. Mechanical Couplings vs. Fluid Couplings:
Fluid couplings use hydraulic fluid to transmit torque between the input and output shafts. They offer smooth torque transmission and can act as a torque limiter, protecting the connected equipment from overloads. However, they have some energy losses due to fluid turbulence, which slightly reduces their efficiency compared to mechanical couplings. Mechanical couplings, on the other hand, provide direct and efficient torque transmission without any energy losses due to fluid friction.
2. Mechanical Couplings vs. Magnetic Couplings:
Magnetic couplings use magnetic fields to transfer torque from one shaft to another. They are commonly used in applications where a hermetic seal is required, such as in pumps and mixers. Magnetic couplings have the advantage of being completely leak-proof, unlike mechanical couplings that may require seals in certain applications. However, magnetic couplings have a lower torque capacity compared to many mechanical couplings, and their efficiency can be affected by variations in magnetic field strength and alignment.
3. Mechanical Couplings vs. Hydraulic Couplings:
Hydraulic couplings use hydraulic fluid to transmit torque. They offer high torque capacity and the ability to slip during overloads, acting as a safety feature. However, hydraulic couplings can have energy losses due to fluid friction, making them slightly less efficient than mechanical couplings. Mechanical couplings do not have energy losses related to fluid friction and provide direct torque transmission, making them more efficient in this regard.
4. Mechanical Couplings vs. Electrical Couplings:
Electrical couplings use electromagnetic fields to transfer torque. They are commonly used in high-precision and high-speed applications, such as robotics and aerospace systems. Electrical couplings can have high torque capacity and precise control over torque transmission. However, they require electrical power to function, which may not be suitable for all applications. Mechanical couplings are self-contained and do not require additional power sources, making them more suitable for various types of machinery and equipment.
5. Mechanical Couplings vs. Friction Couplings:
Friction couplings use friction between contacting surfaces to transmit torque. They are simple in design and can slip during overloads, providing protection against excessive loads. However, friction couplings can experience wear and require periodic maintenance. Mechanical couplings, depending on their type, may have a more robust design and may not experience as much wear under normal operating conditions.
In summary, mechanical couplings offer direct and efficient torque transmission without energy losses related to fluid friction or magnetic fields. While other coupling types may have specific advantages in certain applications, mechanical couplings remain a versatile and widely used choice in various industries due to their reliability, simplicity, and ease of maintenance.
“`
Real-world examples of mechanical coupling applications in different industries.
Mechanical couplings play a vital role in numerous industries, connecting shafts and transmitting torque between various mechanical components. Here are some real-world examples of mechanical coupling applications in different industries:
1. Manufacturing Industry:
In manufacturing plants, mechanical couplings are used in conveyor systems to connect motors to rollers or pulleys, enabling the movement of materials along assembly lines. They are also found in machine tools, such as lathes and milling machines, to transmit torque from the motor to the cutting tools.
2. Automotive Industry:
In the automotive sector, mechanical couplings are used in the powertrain to connect the engine to the transmission and wheels. They enable the transmission of torque from the engine to the wheels, allowing the vehicle to move. Couplings like universal joints (U-joints) are used in the drive shaft to accommodate the misalignment between the engine and the rear axle.
3. Aerospace Industry:
In the aerospace industry, mechanical couplings are used in aircraft engines to transmit torque from the turbine to the propellers or fans. They are also found in flight control systems to connect the pilot’s controls to the aircraft’s control surfaces, allowing for precise maneuvering.
4. Marine Industry:
In ships and boats, mechanical couplings are used in propulsion systems to connect the engine to the propeller shaft. They are also found in steering systems to connect the steering wheel to the rudder, enabling navigation and control of the vessel.
5. Oil and Gas Industry:
In the oil and gas sector, mechanical couplings are used in pumps and compressors to connect the electric motor or engine to the rotating shaft, facilitating the pumping or compression of fluids and gases. They are also used in drilling equipment to transmit torque from the drilling motor to the drill bit.
6. Mining Industry:
In mining operations, mechanical couplings are used in conveyors to transport mined materials, connecting motors to conveyor belts. They are also used in crushers and grinding mills to transmit torque from the motors to the crushing or grinding equipment.
7. Renewable Energy Industry:
In renewable energy applications, mechanical couplings are used in wind turbines to connect the rotor blades to the main shaft, enabling the conversion of wind energy into electricity. They are also used in hydroelectric power plants to connect the turbines to the generators.
8. Construction Industry:
In construction equipment, mechanical couplings are used in excavators, bulldozers, and other machinery to transmit torque from the engine to the hydraulic pumps and other working components.
These are just a few examples of how mechanical couplings are used across various industries to ensure efficient power transmission and smooth operation of a wide range of mechanical systems and equipment.
“`
What is a spline coupling?
A spline coupling is a type of mechanical coupling used to connect two shafts, allowing torque transmission between them while allowing a small amount of relative movement or misalignment. The term “spline” refers to the ridges or teeth on the coupling’s inner or outer surface, which engage with corresponding ridges or grooves on the shafts.
Spline couplings are commonly used in applications where precise torque transmission, rotational alignment, and axial movement are required. They offer several advantages:
1. Torque Transmission:
By using the interlocking ridges or teeth, spline couplings provide a secure connection between the shafts, ensuring efficient torque transfer from one shaft to the other.
2. Misalignment Compensation:
Spline couplings can accommodate a small amount of angular and parallel misalignment between the connected shafts, allowing flexibility in the mechanical system and reducing stress on bearings and other components.
3. Axial Movement:
Some spline couplings, such as spline shafts, allow limited axial movement, making them suitable for applications where shafts may experience thermal expansion or contraction.
4. High Precision:
Spline couplings provide high precision and repeatability in motion control applications. They are commonly used in robotics, machine tools, and automotive transmissions.
5. Different Types:
There are various types of spline couplings, including involute splines, straight-sided splines, and serrated splines, each with different designs and applications.
It is important to note that spline couplings require precise machining and assembly to ensure proper engagement and torque transmission. They are typically used in applications where high torque, precision, and flexibility are necessary for the system’s performance.
“`

editor by CX 2023-11-09
China Good quality L150 Flexible Jaw Couplings for Shaft Connection coupling cdl
Product Description
SYPT L150 Jaw Type couplings are offered in the industry’s largest variety of stock bore/keyway combinations.
These couplings require no lubrication and provide highly reliable service for light, medium, and heavy duty electrical motor and internal combustion power transmission applications.
Now we provide 3 different kinds of the inserts,rubber,urethane and hytrel,color can be made to order..
For the hubs,commom material is GG25 and aluminum.
Please contact us to learn more.
ZheJiang shine transmission machinery Co., Ltd is specialized in manufacturing and selling transmission products. Our products are exported to the world famous machinery company in Europe, America, South Africa, Australia, southeast Asia etc.
Our main products include: European pulley, American pulley, couplings, taper bushing, qd bush, lock element, adjustable motor base, motor rail, sprockets, chain, bolt on hubs, weld on hubs, jaw crusher equipment & spare parts and all kinds of non-standard Casting products etc.
The good quality of our products is demonstrated in various machinery equipment. For example, mining equipment, grain equipment, fan, air compressor, vacuum pump, woodworking machinery, papermaking machinery, mixing equipment etc.
Our slogan is”qualified products win customers, good service benefits customers”. By establishing a closer cooperation with old and new clients, We’ Ll be able to guarantee a CZPT situation develop and progress together.
| Structure: | Flexible |
|---|---|
| Material: | Cast Iron |
| Type: | Jaw |
| Brand: | Sypt |
| Material Choice of Hubs: | Gg25, Steel |
| Material of Spider: | NBR, Urethane, Hytrel for Jaw Coupling |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Types of Couplings
A coupling is a device used to join two shafts together and transmit power. Its purpose is to join rotating equipment while permitting a degree of end movement and misalignment. There are many types of couplings, and it is important to choose the right one for your application. Here are a few examples of couplings.
Mechanical
The mechanical coupling is an important component in power transmission systems. These couplings come in various forms and can be used in different types of applications. They can be flexible or rigid and operate in compression or shear. In some cases, they are permanently attached to the shaft, while in other cases, they are removable for service.
The simplest type of mechanical coupling is the sleeve coupling. It consists of a cylindrical sleeve with an internal diameter equal to the diameter of the shafts. The sleeve is connected to the shafts by a key that restricts their relative motion and prevents slippage. A few sleeve couplings also have threaded holes to prevent axial movement. This type of coupling is typically used for medium to light-duty torque.
Another type of mechanical coupling is a jaw coupling. It is used in motion control and general low-power transmission applications. This type of coupling does not require lubrication and is capable of accommodating angular misalignment. Unlike other types of couplings, the jaw coupling uses two hubs with intermeshing jaws. The jaw coupling’s spider is typically made of copper alloys. In addition, it is suitable for shock and vibration loads.
Mechanical couplings can be made from a variety of materials. One popular choice is rubber. The material can be natural or chloroprene. These materials are flexible and can tolerate slight misalignment.
Electrical
Electrical coupling is the process in which a single electrical signal is transferred from a nerve cell to another. It occurs when electrical signals from two nerve cells interact with each other in a way similar to haptic transmission. This type of coupling can occur on its own or in combination with electrotonic coupling in gap junctions.
Electrical coupling is often associated with oscillatory behavior of neurons. The mechanism of electrical coupling is complex and is studied mathematically to understand its effect on oscillatory neuron networks. For example, electrical coupling can increase or decrease the frequency of an oscillator, depending on the state of the neuron coupled to it.
The site of coupling is usually the junction of opposing cell membranes. The cellular resistance and the coupling resistance are measured in voltage-clamp experiments. This type of coupling has a specific resistance of 100 O-cm. As a result, the coupling resistance varies with the frequency.
The authors of this study noted that electrotonic coupling depends on the ratio between the resistance of the nonjunctional membranes and the junctional membranes. The voltage attenuation technique helps reveal the differences in resistance and shunting through the intercellular medium. However, it is unclear whether electrotonic coupling is electrostatically mediated.
Electrical coupling has also been suggested to play a role in the intercellular transfer of information. There are many examples that support this theory. A message can be a distinct qualitative or quantitative signal, which results in a gradient in the cells. Although gap junctions are absent at many embryonic interaction sites, increasing evidence suggests a role in information transfer.
Flexible
When it comes to choosing the right Flexible Coupling, there are several factors that you should take into account. Among these factors is the backlash that can be caused by the movement of the coupling. The reason for this problem is the fact that couplings that do not have anti-fungal properties can be easily infected by mold. The best way to avoid this is to pay attention to the moisture content of the area where you are installing the coupling. By following these guidelines, you can ensure the best possible installation.
To ensure that you are getting the most out of your flexible couplings, you must consider their characteristics and how easy they are to install, assemble, and maintain. You should also look for elements that are field-replaceable. Another important factor is the coupling’s torsional rigidity. It should also be able to handle reactionary loads caused by misalignment.
Flexible couplings come in many different types. There are diaphragm and spiral couplings. These couplings allow for axial motion, angular misalignment, and parallel offset. They have one-piece construction and are made from stainless steel or aluminum. These couplings also offer high torsional stiffness, which is beneficial for applications requiring high torques.
Flexible couplings have several advantages over their rigid counterparts. They are designed to handle misalignments of up to seven degrees and 0.025 inches. These characteristics are important in motion control applications. Flexible couplings are also inexpensive, and they do not require maintenance.
Beam
A beam coupling is a type of mechanical coupling, usually one solid piece, that connects two mechanical parts. Its performance is largely determined by the material used. Typical materials include stainless steel, aluminum, Delrin, and titanium. The beam coupling is rated for different speeds and torques. The coupling should be selected according to the application. In addition to the material, the application should also consider the speed and torque of the system.
There are two main types of beam couplings. The first is the helical beam coupling, which has a continuous multi spiral cut. This type of coupling offers a high degree of flexibility and compensates for a high degree of misalignment. The second type of beam coupling is the helical shaft coupling, which has a low torsional stiffness, which makes it ideal for small torque applications.
Another type of beam coupling is the multiple beam design, which combines two beams. It allows for more tolerance in manufacturing and installation and protects expensive components from excessive bearing loads. It also helps keep beams shorter than a single beam coupling. This type of coupling also enables a higher torque capacity and torsional stiffness.
Beam couplings can be manufactured with different materials, including stainless steel and aluminum. The “A” series is available in aluminum and stainless steel and is ideal for general-purpose and light-duty applications. It is also economical and durable. This type of coupling can also be used with low torque pumps or encoder/resolver systems.
Pin & bush
The Pin & bush coupling is a versatile, general-purpose coupling with high tensile bolts and rubber bushes. It can tolerate a wide range of operating temperatures and is suitable for use in oil and water-resistance applications. Its unique design enables it to be used in either direction. In addition, it requires no lubrication.
The pin bush coupling is a fail-safe coupling with a long service life and is used for high-torque applications. It provides torsional flexibility and dampens shocks, making it a flexible coupling that protects equipment and reduces maintenance costs. Its hubs are forged from graded cast iron for strength and durability. Besides, the coupling’s elastomer elements reduce vibration and impact loads. It also accommodates a misalignment of up to 0.5 degrees.
Pin & bush couplings are a popular choice for a variety of different applications. This coupling features a protective flange design that protects the coupling flange from wear and tear. The coupling nut is secured to one flange, while a rubber or leather bush sits between the other flange. Its unique design makes it ideal for use in applications where misalignment is a small factor. The rubber bushing also helps absorb vibration and shock.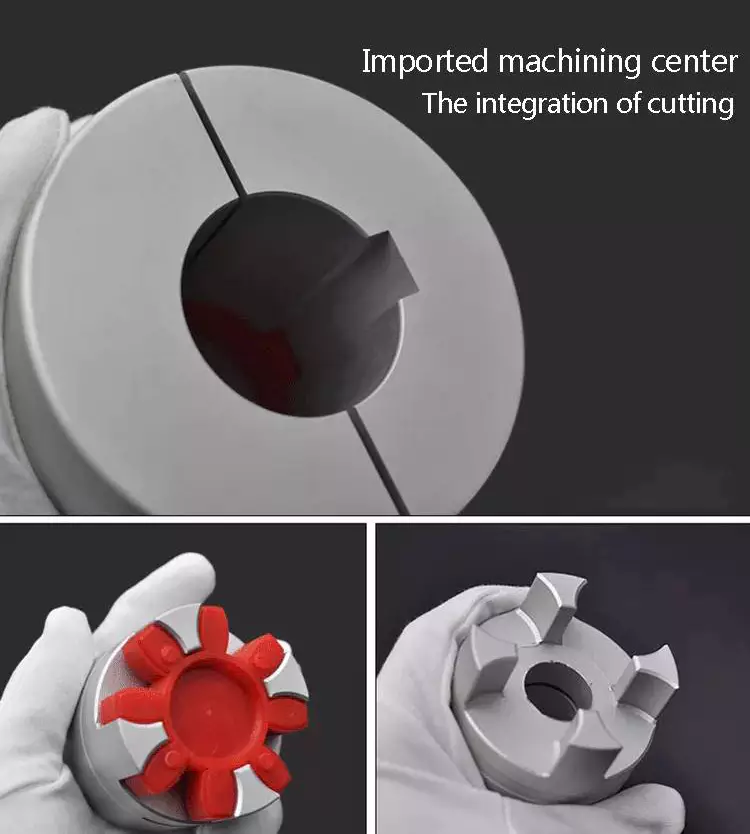
Mesh tooth
Mesh tooth couplings are used to transfer torque between two shafts and reduce backlash. However, mesh tooth couplings have some limitations. One disadvantage is the break-away friction factor in the axial direction. This problem is caused by the high contact force between the tooth and gear mesh. This can cause unpredictable forces on the shafts.
In this paper, we present a FEM model for mesh tooth coupling. We first validate the mesh density. To do so, we compute the bolt stress as a uniaxial tensile during the tightening process. We used different mesh sizes and mesh density to validate our results.
The mesh stiffness of gear pairs is influenced by lead crown relief and misalignment. For example, if one tooth is positioned too far in the axis, the mesh stiffness will be decreased. A misaligned gear pair will lose torque capacity. A mesh tooth coupling can be lubricated with oil.
An ideal mesh tooth coupling has no gaps between the teeth, which reduces the risk of uneven wear. The coupling’s quality exposed fasteners include SAE Grade 5 bolts. It also offers corrosion resistance. The couplings are compatible with industrial environments. They also eliminate the need for selective assembly in sleeve couplings.

editor by CX 2023-06-14
China supplier tar disc stainless steel shaft diaphragm flexible disc couplings flexible shaft coupling
Warranty: 3 several years
Applicable Industries: Producing Plant, Equipment Restore Outlets, Construction operates
Customized help: OEM
Structure: Gear
Adaptable or Rigid: Flexible
Standard or Nonstandard: Nonstandard
Content: Stainless metal
Physique Materials: SS304/316L
Dimensions: customzied
Packaging Particulars: Wrap by Plastic movie then waterproof paper, last but not least the wood situation
Port: ZheJiang
tar disc stainless metal diaphragm adaptable elastic coupling
Couplings are mechanical fasteners, normally used to be a part of 2 parts of a shaft together for the function of driving rotating tools. Many shaft coupling are created for tight tolerances and need really accurate shaft alignment. A diaphragm coupling is a sort of flexible coupling that makes use of a pair of versatile plates joined by a spacer to transfer torque from 1 plate to the other. The overall flexibility of the diaphragm plates enable for slight misalignments.
How to Determine the Quality of a Worm Shaft
There are many advantages of a worm shaft. It is easier to manufacture, as it does not require manual straightening. Among these benefits are ease of maintenance, reduced cost, and ease of installation. In addition, this type of shaft is much less prone to damage due to manual straightening. This article will discuss the different factors that determine the quality of a worm shaft. It also discusses the Dedendum, Root diameter, and Wear load capacity.
Root diameter
There are various options when choosing worm gearing. The selection depends on the transmission used and production possibilities. The basic profile parameters of worm gearing are described in the professional and firm literature and are used in geometry calculations. The selected variant is then transferred to the main calculation. However, you must take into account the strength parameters and the gear ratios for the calculation to be accurate. Here are some tips to choose the right worm gearing.
The root diameter of a worm gear is measured from the center of its pitch. Its pitch diameter is a standardized value that is determined from its pressure angle at the point of zero gearing correction. The worm gear pitch diameter is calculated by adding the worm’s dimension to the nominal center distance. When defining the worm gear pitch, you have to keep in mind that the root diameter of the worm shaft must be smaller than the pitch diameter.
Worm gearing requires teeth to evenly distribute the wear. For this, the tooth side of the worm must be convex in the normal and centre-line sections. The shape of the teeth, referred to as the evolvent profile, resembles a helical gear. Usually, the root diameter of a worm gear is more than a quarter inch. However, a half-inch difference is acceptable.
Another way to calculate the gearing efficiency of a worm shaft is by looking at the worm’s sacrificial wheel. A sacrificial wheel is softer than the worm, so most wear and tear will occur on the wheel. Oil analysis reports of worm gearing units almost always show a high copper and iron ratio, suggesting that the worm’s gearing is ineffective.
Dedendum
The dedendum of a worm shaft refers to the radial length of its tooth. The pitch diameter and the minor diameter determine the dedendum. In an imperial system, the pitch diameter is referred to as the diametral pitch. Other parameters include the face width and fillet radius. Face width describes the width of the gear wheel without hub projections. Fillet radius measures the radius on the tip of the cutter and forms a trochoidal curve.
The diameter of a hub is measured at its outer diameter, and its projection is the distance the hub extends beyond the gear face. There are two types of addendum teeth, one with short-addendum teeth and the other with long-addendum teeth. The gears themselves have a keyway (a groove machined into the shaft and bore). A key is fitted into the keyway, which fits into the shaft.
Worm gears transmit motion from two shafts that are not parallel, and have a line-toothed design. The pitch circle has two or more arcs, and the worm and sprocket are supported by anti-friction roller bearings. Worm gears have high friction and wear on the tooth teeth and restraining surfaces. If you’d like to know more about worm gears, take a look at the definitions below.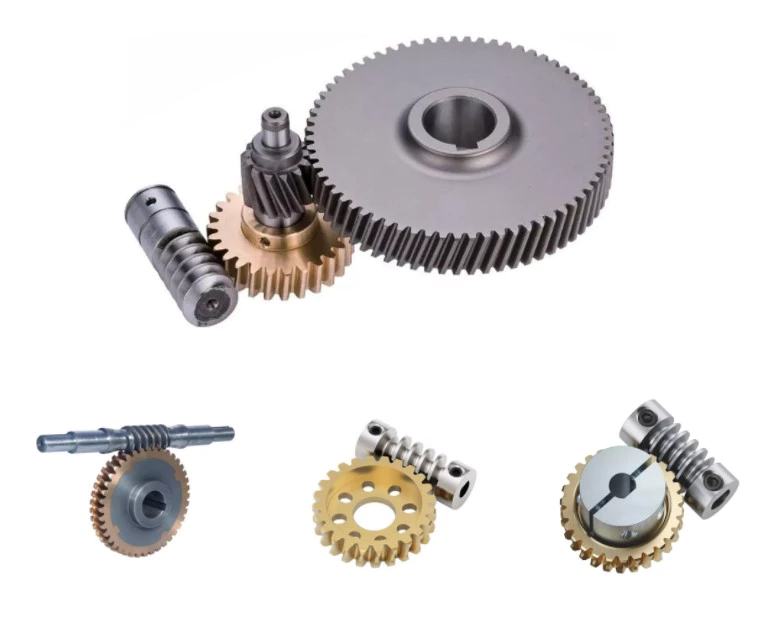
CZPT’s whirling process
Whirling process is a modern manufacturing method that is replacing thread milling and hobbing processes. It has been able to reduce manufacturing costs and lead times while producing precision gear worms. In addition, it has reduced the need for thread grinding and surface roughness. It also reduces thread rolling. Here’s more on how CZPT whirling process works.
The whirling process on the worm shaft can be used for producing a variety of screw types and worms. They can produce screw shafts with outer diameters of up to 2.5 inches. Unlike other whirling processes, the worm shaft is sacrificial, and the process does not require machining. A vortex tube is used to deliver chilled compressed air to the cutting point. If needed, oil is also added to the mix.
Another method for hardening a worm shaft is called induction hardening. The process is a high-frequency electrical process that induces eddy currents in metallic objects. The higher the frequency, the more surface heat it generates. With induction heating, you can program the heating process to harden only specific areas of the worm shaft. The length of the worm shaft is usually shortened.
Worm gears offer numerous advantages over standard gear sets. If used correctly, they are reliable and highly efficient. By following proper setup guidelines and lubrication guidelines, worm gears can deliver the same reliable service as any other type of gear set. The article by Ray Thibault, a mechanical engineer at the University of Virginia, is an excellent guide to lubrication on worm gears.
Wear load capacity
The wear load capacity of a worm shaft is a key parameter when determining the efficiency of a gearbox. Worms can be made with different gear ratios, and the design of the worm shaft should reflect this. To determine the wear load capacity of a worm, you can check its geometry. Worms are usually made with teeth ranging from one to four and up to twelve. Choosing the right number of teeth depends on several factors, including the optimisation requirements, such as efficiency, weight, and centre-line distance.
Worm gear tooth forces increase with increased power density, causing the worm shaft to deflect more. This reduces its wear load capacity, lowers efficiency, and increases NVH behavior. Advances in lubricants and bronze materials, combined with better manufacturing quality, have enabled the continuous increase in power density. Those three factors combined will determine the wear load capacity of your worm gear. It is critical to consider all three factors before choosing the right gear tooth profile.
The minimum number of gear teeth in a gear depends on the pressure angle at zero gearing correction. The worm diameter d1 is arbitrary and depends on a known module value, mx or mn. Worms and gears with different ratios can be interchanged. An involute helicoid ensures proper contact and shape, and provides higher accuracy and life. The involute helicoid worm is also a key component of a gear.
Worm gears are a form of ancient gear. A cylindrical worm engages with a toothed wheel to reduce rotational speed. Worm gears are also used as prime movers. If you’re looking for a gearbox, it may be a good option. If you’re considering a worm gear, be sure to check its load capacity and lubrication requirements.
NVH behavior
The NVH behavior of a worm shaft is determined using the finite element method. The simulation parameters are defined using the finite element method and experimental worm shafts are compared to the simulation results. The results show that a large deviation exists between the simulated and experimental values. In addition, the bending stiffness of the worm shaft is highly dependent on the geometry of the worm gear toothings. Hence, an adequate design for a worm gear toothing can help reduce the NVH (noise-vibration) behavior of the worm shaft.
To calculate the worm shaft’s NVH behavior, the main axes of moment of inertia are the diameter of the worm and the number of threads. This will influence the angle between the worm teeth and the effective distance of each tooth. The distance between the main axes of the worm shaft and the worm gear is the analytical equivalent bending diameter. The diameter of the worm gear is referred to as its effective diameter.
The increased power density of a worm gear results in increased forces acting on the corresponding worm gear tooth. This leads to a corresponding increase in deflection of the worm gear, which negatively affects its efficiency and wear load capacity. In addition, the increasing power density requires improved manufacturing quality. The continuous advancement in bronze materials and lubricants has also facilitated the continued increase in power density.
The toothing of the worm gears determines the worm shaft deflection. The bending stiffness of the worm gear toothing is also calculated by using a tooth-dependent bending stiffness. The deflection is then converted into a stiffness value by using the stiffness of the individual sections of the worm shaft. As shown in figure 5, a transverse section of a two-threaded worm is shown in the figure.


editor by czh